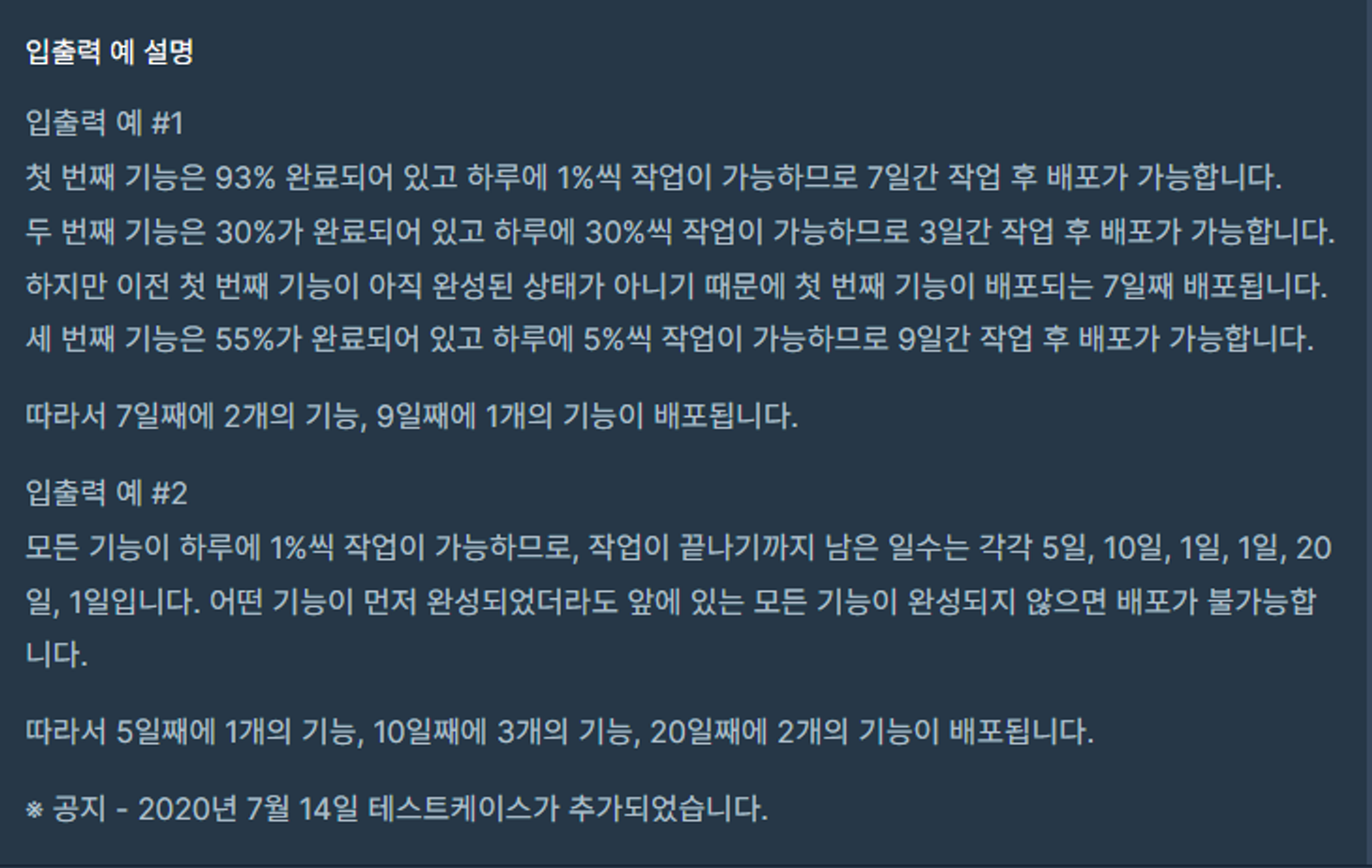
문제

코딩
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
vector<int> solution(vector<int> progresses, vector<int> speeds) {
vector<int> answer;
int imaxday = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < progresses.size(); ++i)
{
int iday = 0;
iday = (int)ceil((float)(100 - progresses[i]) / speeds[i]);
if (imaxday < iday)
{
imaxday = iday;
answer.push_back(1);
}
else
{
answer.back() += 1;
}
}
return answer;
}더보기
Note
float에서 int를 강제 케스팅 하면, 소수점을 제외한 정수형으로 출력된다. 즉, 5.2 → 5, 5.8 → 5로 된다.
올림 함수 ceil()은 cmath 라이브러리를 참조해야 한다.
vector의 멤버함수 vector.back()은 가장 마지막 원소를 참조한다.
2024.04.24
원래 코드는 11번 케이스가 통과하지 못했는데,
iday = (int)ceil((100 - progresses[i]) / speeds[i]);
이 코드에서 progresses[]와 speed[]가 int 자료형이기 때문에 해당 계산 결과가 int로 형변환 되면서 내림이 되어버리고, 내림된 정수가 ceil()의 인자로 들어가면서 원래 의도했던, 올림이 되지 않았었다.
때문에 해당 코드를
iday = (int)ceil((float)(100 - progresses[i]) / speeds[i]);로 수정해 해결해 주었다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct tNode
{
int iCurProgress;
int iIdx;
int iLoofCount;
tNode(int i_Progress, int i_Idx, int i_Loof)
: iCurProgress(i_Progress)
, iIdx(i_Idx)
, iLoofCount(i_Loof) {}
};
vector<int> solution(vector<int> progresses, vector<int> speeds)
{
vector<int> answer;
queue<tNode> q;
for (size_t i = 0; i < progresses.size(); ++i)
{
q.push(tNode(progresses[i], i, 0));
}
int iPrevLoofCount = -1;
bool bCheck = false;
while (!q.empty())
{
auto iCurNode = q.front();
q.pop();
int iNewProgress = iCurNode.iCurProgress + speeds[iCurNode.iIdx];
int iCurLoofCount = iCurNode.iLoofCount;
if (iPrevLoofCount != iCurLoofCount)
{
if (100 <= iNewProgress)
{
bCheck = true;
answer.push_back(1);
}
else
{
q.push(tNode(iNewProgress, iCurNode.iIdx, iCurLoofCount + 1));
}
iPrevLoofCount = iCurLoofCount;
}
else
{
if (100 <= iNewProgress && bCheck)
{
answer.back() += 1;
}
else
{
q.push(tNode(iNewProgress, iCurNode.iIdx, iCurLoofCount + 1));
bCheck = false;
}
}
}
return answer;
}더보기
2024.04.24
본래 의도대로 queue를 이용해 풀어보았다.
구조는 쉽게 생각해서 잡긴했는데, if문 분기 처리 하는게 생각하는게 조금 시간이 걸렸다.
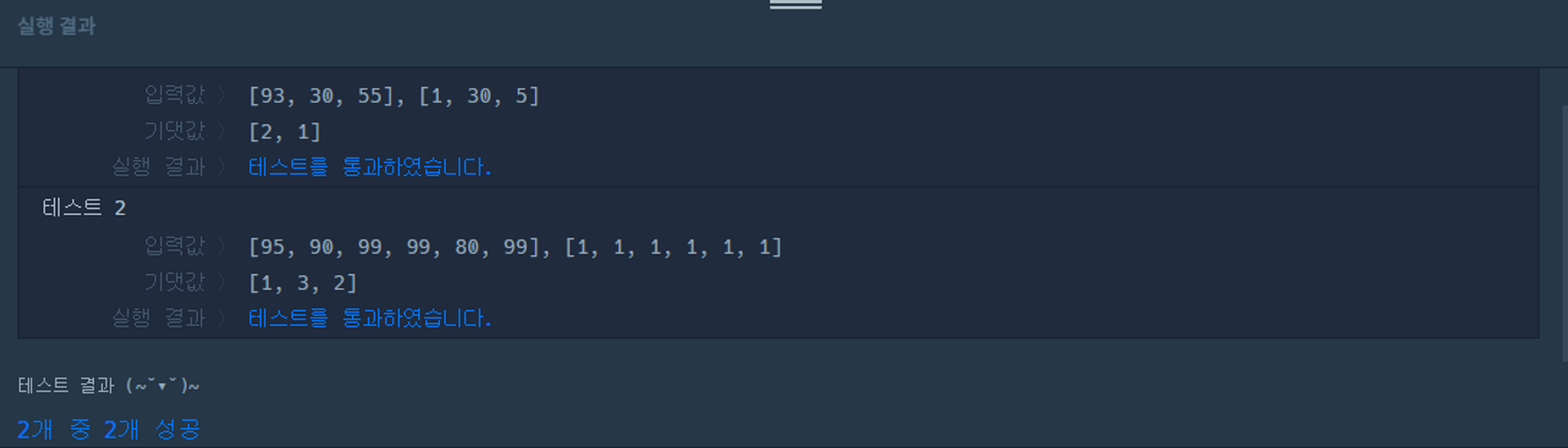
실행 결과
'프로그래밍 > 코딩 문제 풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프로그래머스 2023.06.12 (1Lv 직사각형 별찍기 / 핸드폰 번호 가리기) (1) | 2023.06.19 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스 2023.06.11 (2Lv 프로세스) (0) | 2023.06.19 |
| 프로그래머스 2023.06.07 (2Lv 광물 캐기) (0) | 2023.06.19 |
| 프로그래머스 2023.06.05 (2Lv 점 찍기) (0) | 2023.06.19 |
| 프로그래머스 2023.06.04 (2Lv 영어 끝말잇기) (0) | 2023.06.19 |



